Product Description:
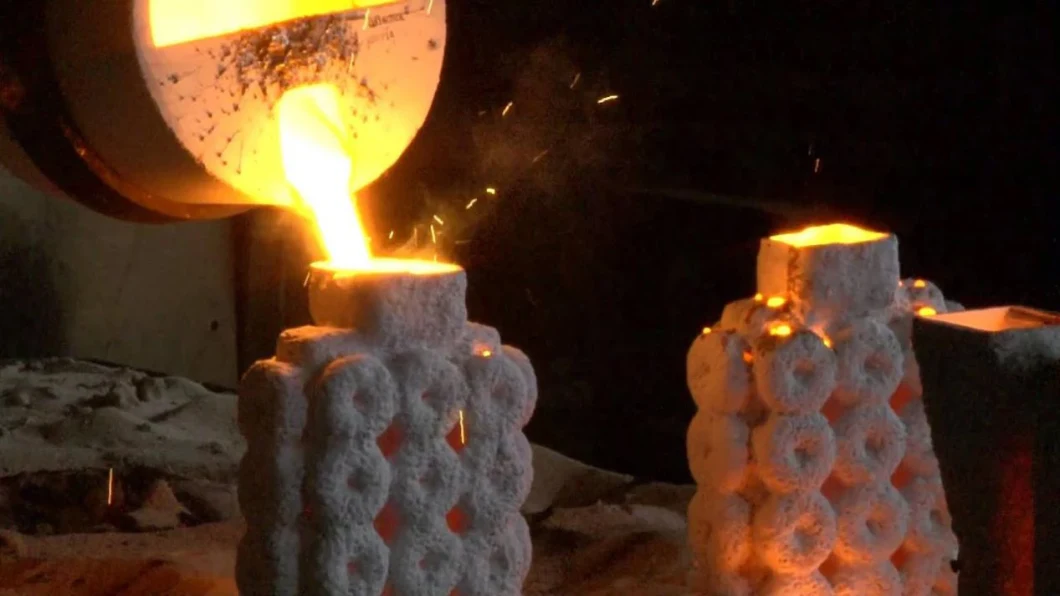

What is casting?
Casting is a manufacturing process in which a liquid material is usually poured into a mold, which contains a hollow cavity of the desired shape, and then allowed to solidify. The solidified part is also known as a casting, which is ejected or broken out of the mold to complete the process. Casting materials are usually metals or various time setting materials that cure after mixing two or more components together; examples are epoxy, concrete, plaster and clay. Casting is most often used for making complex shapes that would be otherwise difficult or uneconomical to make by other methods.Heavy equipment like machine tool beds,ship's propeller etc. can be cast easily in the required size rather than fabricating them by joining several small pieces.
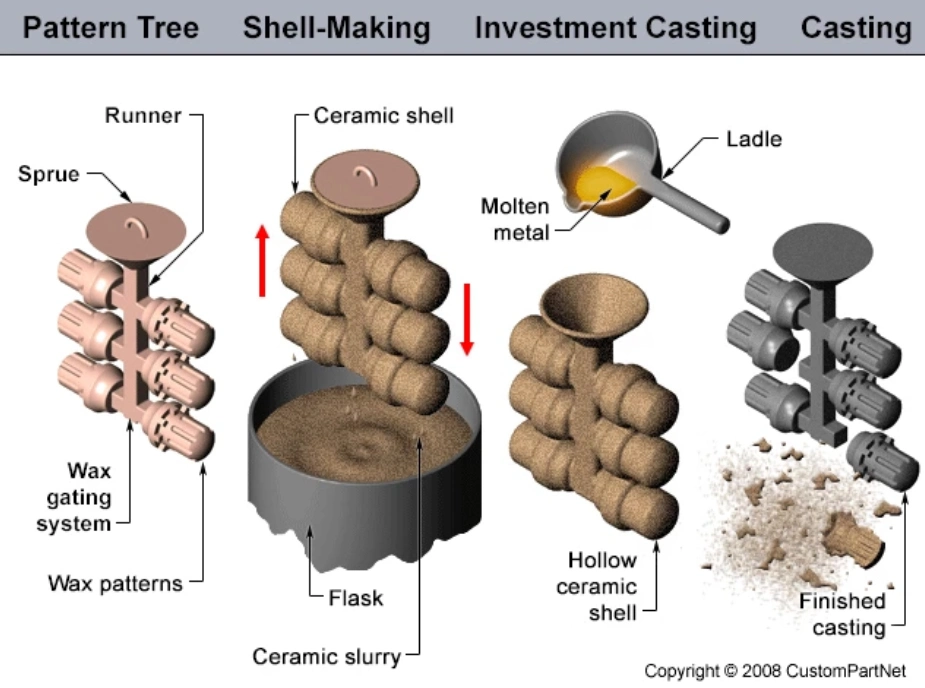
Casting (metalworking)
In metalworking, metal is heated until it becomes liquid and is then poured into a mold. The mold is a hollow cavity that includes the desired shape, but the mold also includes runners and risers that enable the metal to fill the mold. The mold and the metal are then cooled until the metal solidifies. The solidified part (the casting) is then recovered from the mold. Subsequent operations remove excess material caused by the casting process (such as the runners and risers).
Fettling can add significantly to the cost of the resulting product, and designers of molds seek to minimize it through the shape of the mold, the material being cast, and sometimes by including decorative elements.
Casting process simulation uses numerical methods to calculate cast component quality considering mold filling, solidification and cooling, and provides a quantitative prediction of casting mechanical properties, thermal stresses and distortion. Simulation accurately describes a cast component's quality up-front before production starts. The casting rigging can be designed with respect to the required component properties. This has benefits beyond a reduction in pre-production sampling, as the precise layout of the complete casting system also leads to energy, material, and tooling savings.
The software supports the user in component design, the determination of melting practice and casting methoding through to pattern and mold making, heat treatment, and finishing. This saves costs along the entire casting manufacturing route.

Why choices us?
1. auto parts, classic car parts
2. machine parts, pump body housing, engine parts, cylinders, pistons, transmission housing.
3. cookware parts, kitchen ware parts.
4. medical equipment parts, housing, instrument housing, I beam, housing...etc.
5. Bicycle and motocycle parts, sport equipment parts, housings, covers, heat sinks.
Our Policy:
Innovation and developing in Technique
High level of expertise
Outstanding quality
On-time delivery to customer needs

PACKAGE:

Transport:


What is casting?
Casting is a manufacturing process in which a liquid material is usually poured into a mold, which contains a hollow cavity of the desired shape, and then allowed to solidify. The solidified part is also known as a casting, which is ejected or broken out of the mold to complete the process. Casting materials are usually metals or various time setting materials that cure after mixing two or more components together; examples are epoxy, concrete, plaster and clay. Casting is most often used for making complex shapes that would be otherwise difficult or uneconomical to make by other methods.Heavy equipment like machine tool beds,ship's propeller etc. can be cast easily in the required size rather than fabricating them by joining several small pieces.

Product Specifications: | |
| Material: | Aluminum, A380, A356, ADC12, AlSi10Mg, 104, 102 etc. |
| Dimension: | According to the drawing or sample |
| Standard: | DIN GB ISO JIS BA ANSI |
| Casting equipment: | 80T/160T/250T/300T/500Tcasting machine,Sand blasting machine,5T electri stove,Metallographic detector,Independent mould manufacturing |
| Production Process: | Polish/Sand Blast/EDM/Milling/Texture/Grind/Pre-Treatment/Quenching/Lathe/Wire Cut/Annealing/Temper etc. |
| Equipment of Casting: | 1. High pressure die casting machining:125T/180T/250T/280T/500T/800T/1250T 2. Gravity casting machine: 5 production lines 3. Low pressure die casting machining: 1 production line 4. Sand casting machine: 6 production lines 5. Degassing equipment and opportunities to refine the material 6. Machining: 5Sets CNC Machines;3 sets Milling machines; 3 setsTurning machines; 10 sets drill and tap machines |
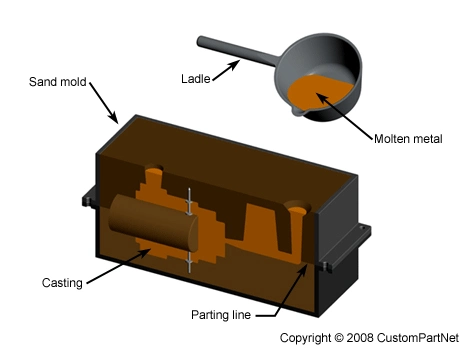
Casting (metalworking)
In metalworking, metal is heated until it becomes liquid and is then poured into a mold. The mold is a hollow cavity that includes the desired shape, but the mold also includes runners and risers that enable the metal to fill the mold. The mold and the metal are then cooled until the metal solidifies. The solidified part (the casting) is then recovered from the mold. Subsequent operations remove excess material caused by the casting process (such as the runners and risers).

Fettling can add significantly to the cost of the resulting product, and designers of molds seek to minimize it through the shape of the mold, the material being cast, and sometimes by including decorative elements.
Casting process simulation uses numerical methods to calculate cast component quality considering mold filling, solidification and cooling, and provides a quantitative prediction of casting mechanical properties, thermal stresses and distortion. Simulation accurately describes a cast component's quality up-front before production starts. The casting rigging can be designed with respect to the required component properties. This has benefits beyond a reduction in pre-production sampling, as the precise layout of the complete casting system also leads to energy, material, and tooling savings.
The software supports the user in component design, the determination of melting practice and casting methoding through to pattern and mold making, heat treatment, and finishing. This saves costs along the entire casting manufacturing route.
| Typical | Feasible | |
| Shapes: | Thin-walled: Complex Solid: Cylindrical Solid: Cubic Solid: Complex | Flat Thin-walled: Cylindrical Thin-walled: Cubic |
| Part size: | Weight: 1 oz - 450 ton | |
| Materials: | Metals Alloy Steel Carbon Steel Cast Iron Stainless Steel Aluminum Copper Magnesium Nickel | Lead Tin Titanium Zinc |
| Surface finish - Ra: | 300 - 600 μin | 125 - 2000 μin |
| Tolerance: | ± 0.03 in. | ± 0.015 in. |
| Max wall thickness: | 0.125 - 5 in. | 0.09 - 40 in. |
| Advantages: | Can produce very large parts Can form complex shapes Many material options Low tooling and equipment cost Scrap can be recycled Short lead time possible | |
| Disadvantages: | Poor material strength High porosity possible Poor surface finish and tolerance Seondary machining often required Low production rate High labor cost | |
| Applications: | Engine blocks and manifolds, machine bases, gears, pulleys | |

Why choices us?
- In China, we have more than 13 years of experience in processing foreign companies for foreign companies.
- China manufacturer in Qingdao,not trade company
- Competitive price and nice service
- ISO/SGS passed
- Application: Automotive,medical device, electronics, toy, furniture, industrial etc.
1. auto parts, classic car parts
2. machine parts, pump body housing, engine parts, cylinders, pistons, transmission housing.
3. cookware parts, kitchen ware parts.
4. medical equipment parts, housing, instrument housing, I beam, housing...etc.
5. Bicycle and motocycle parts, sport equipment parts, housings, covers, heat sinks.
Our Policy:
Innovation and developing in Technique
High level of expertise
Outstanding quality
On-time delivery to customer needs

PACKAGE:

Transport:
